

A conflict might arise because the number is generated arbitrarily, but considering the range of value from -9223372036854775808 to 9223372036854775807, this is unlikely to happen. Pinpoint can find associated n Spans using a TransactionId and can sort them as a hierarchical tree structure using a SpanId and a ParentSpanId.Ī SpanId and a ParentSpanId are 64-bit long integers. A ParentSpanId indicates the SpainId of a parent that makes RPC calls. You can think of a SpanId as a thread which handles HTTP requests. To identify the relationships between RPCs, a SpanId and a ParentSpanId (pSpanId) are required. However, a TransactionId itself can’t explicitly describe the relationship between RPCs. The figure below illustrates the behavior of a TraceId in which RPCs were made 3 times within 4 nodes.Ī TransactionId (TxId) represents that three different RPCs are associated with each other as a single transaction in Figure 2. The term “TransactionId” in Pinpoint has the same meaning as the term “TraceId” in Google’s Dapper and the term “TraceId” in Pinpoint refers to a collection of keys. If a node is the starting point of a transaction, there will not be a parent span - for these cases, we use a value of -1 to denote that the span is the root span of a transaction.ĭifferences in terms between Google’s Dapper and NAVER’s Pinpoint
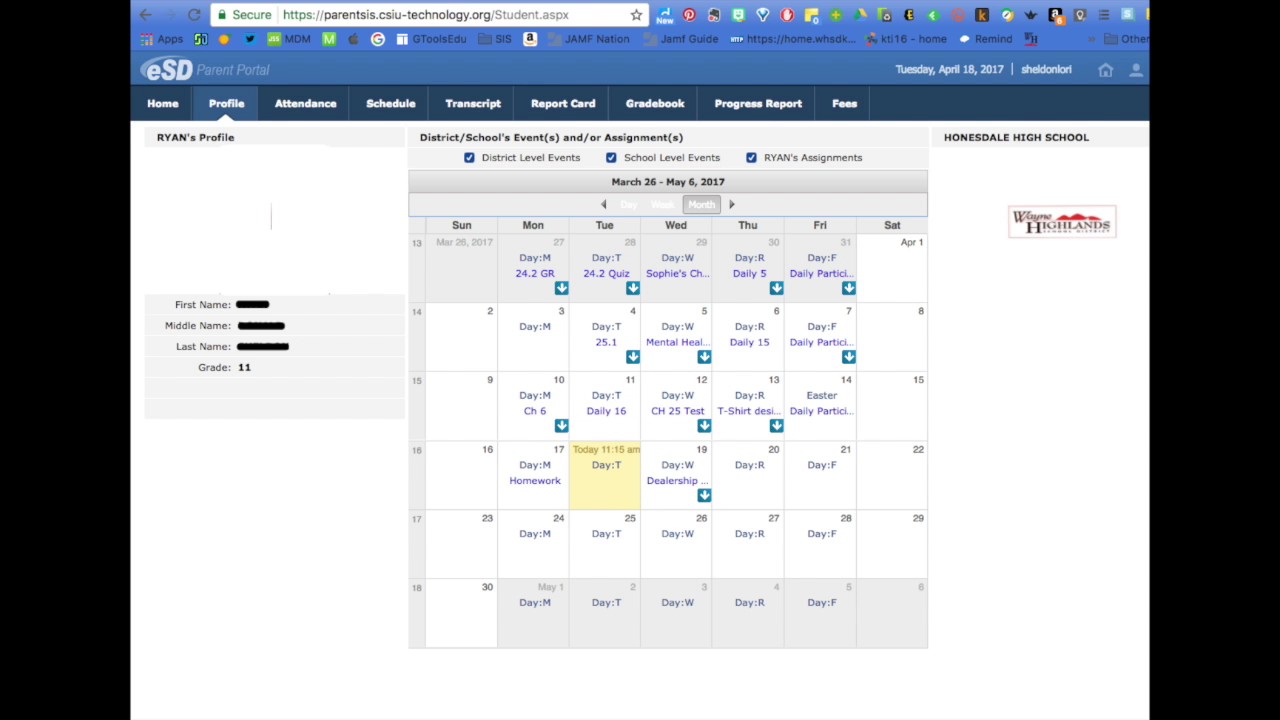
SpanId: The ID of a job processed when receiving RPC messages it is generated when an RPC arrives at a node.TransactionId (TxId): The ID of the message sent/received across distributed systems from a single transaction it must be globally unique across the entire group of servers.The TransactionId indicates the message ID, and both the SpanId and the ParentSpanId represent the parent-child relationship of RPCs. TraceId: A collections of keys consisting of TransactionId, SpanId, and ParentSpanId.

A Trace is sorted as a hierarchical tree structure through SpanIds and ParentSpanIds. Spans in the same trace share the same TransactionId. Trace: A collection of Spans it consists of associated RPCs (Spans).To ensure the code-level visibility, a Span has children labeled SpanEvent as a data structure. Span: The basic unit of RPC (remote procedure call) tracing it indicates work processed when an RPC arrives and contains trace data.In Pinpoint, the core of data structure consists of Spans, Traces, and TraceIds. The tag data consists of a collection of keys, which is defined as a TraceId. Pinpoint is modeled on the tracing technique of Google’s Dapper but has been modified to add application-level tag data in the call header to trace distributed transactions at a remote call. For example, it includes tag information for a message in the HTTP header at an HTTP request and traces the message using this tag.įor more information on Google’s Dapper, see “ Dapper, a Large-Scale Distributed Systems Tracing Infrastructure.” The solution is to add application-level tags that can be a link between messages when sending a message. However, a simple solution to resolve such issues has been implemented in Google’s Dapper. In addition, it was difficult to accurately trace messages. However, implementation complexity was high with low performance because it should be implemented separately for each protocol. An attempt was made to trace messages at TCP or operating system level. In other words, when X-th message is sent from Node 1, the X-th message cannot be identified among N’ messages received in Node 2. For example, we cannot recognize relationships between N messages sent from Node 1 and N’ messages received in Node 2.
The problem is that there is no way to identify relationships between messages. Message relationship in a distributed system The purpose of a distributed tracing system is to identify relationships between Node 1 and Node 2 in a distributed system when a message is sent from Node 1 to Node 2 (Figure 1).įigure 1. How Distributed Transaction Tracing Works in Google’s Dapper Pinpoint traces distributed requests in a single transaction, modeled after Google’s Dapper. Distributed Transaction Tracing, Modeled after Google’s Dapper And we explain the optimization method applied to Pinpoint Agent, which modifies bytecode and record performance data. In this article, we describe the Pinpoint’s techniques such as transaction tracing and bytecode instrumentation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
